 Tests for Glaucoma
Tests for Glaucoma
Glaucoma Diagnostic Tests
Glaucoma is detected through a series of special tests as well as a general comprehensive eye exam that includes:
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT Scan)
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT Scan) Can Diagnose Glaucoma Before All Other Tests. It is arguably the most accurate test in the world to assist our doctors in diagnosing glaucoma.
GDxVCC Scanning Laser Polarimetry

GDxVCC Scanning Laser Polarimetry: This is also one of the world’s most accurate single tests in diagnosing glaucoma. Along with the OCT scan, this is the only type of technology available that directly and objectively evaluates the retinal nerve fiber layer of the eye, which is the specific site of damage from glaucoma. OCT and GDxVCC can detect nerve fiber layer loss approximately six years before visual field loss.
Scanning Laser Polarimetry or an OCT scan is a must in diagnosing and monitoring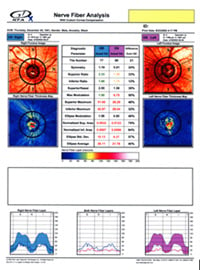 glaucoma. The newest spectral domain OCT used by Master Eye Associates' optometric glaucoma specialists provides even better diagnostic capabilities than the GDx or the Stratus OCT because our new OCT can monitor progression of retinal nerve fiber loss over time. Only the newest spectral domain OCT can monitor progressive loss of the nerve fiber layer. That function is crucial in monitoring glaucoma, which by its very nature is a disease of progression.
glaucoma. The newest spectral domain OCT used by Master Eye Associates' optometric glaucoma specialists provides even better diagnostic capabilities than the GDx or the Stratus OCT because our new OCT can monitor progression of retinal nerve fiber loss over time. Only the newest spectral domain OCT can monitor progressive loss of the nerve fiber layer. That function is crucial in monitoring glaucoma, which by its very nature is a disease of progression.
At Master Eye Associates we believe that having the best technology is a way of showing that we care about our patients.
Visual acuity test. This eye chart test measures how well you see at various distances.
Visual field test. This test measures your central and peripheral vision  area. It helps tell if you have reduced visual sensitivity to certain areas within your visual field as well as lost visual field areas called scotomas. Although this test is useful and still the most used test in diagnosing glaucoma it is not as accurate in diagnosing early glaucoma as the GDxVCC. Unfortunately, up to 60 percent of nerve fibers may be diminished or damaged before visual field analysis can identify a problem.
area. It helps tell if you have reduced visual sensitivity to certain areas within your visual field as well as lost visual field areas called scotomas. Although this test is useful and still the most used test in diagnosing glaucoma it is not as accurate in diagnosing early glaucoma as the GDxVCC. Unfortunately, up to 60 percent of nerve fibers may be diminished or damaged before visual field analysis can identify a problem.
Remember, the OCT scan or our GDxVCC threshold exam can identify glaucoma up to six years before the problem is identified on the visual field test.
Dilated eye exam. Drops are placed in your eyes to widen, or dilate, the pupils. Your eye care professional uses a special magnifying lens to examine your retina and optic nerve for signs of damage and other eye problems. After the exam, your close-up vision may remain blurred for  several hours.
several hours.
Tonometry. An instrument called a tonometer measures the pressure inside the eye. There are several different methods to test the fluid pressure inside the eyes. The newest tonometer takes into account the many biomechanical properties of the cornea that influence intraocular pressure.
Pachymetry. A numbing drop is applied to your eye. Your eye care professional uses an ultrasonic wave instrument to measure the thickness of your cornea. It is now well documented by a major national study (Ocular Hypertension and Treatment Study OHTS) that thinner than average corneas are a definite risk factor for glaucoma. This test can also be performed using optical coherence tomography instead of ultrasound.
of your cornea. It is now well documented by a major national study (Ocular Hypertension and Treatment Study OHTS) that thinner than average corneas are a definite risk factor for glaucoma. This test can also be performed using optical coherence tomography instead of ultrasound.

